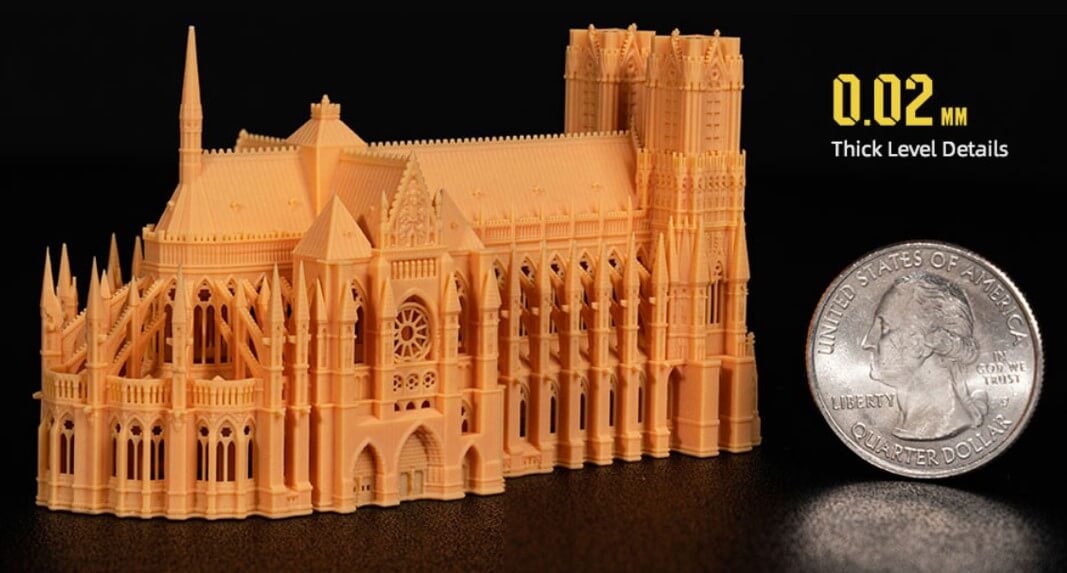
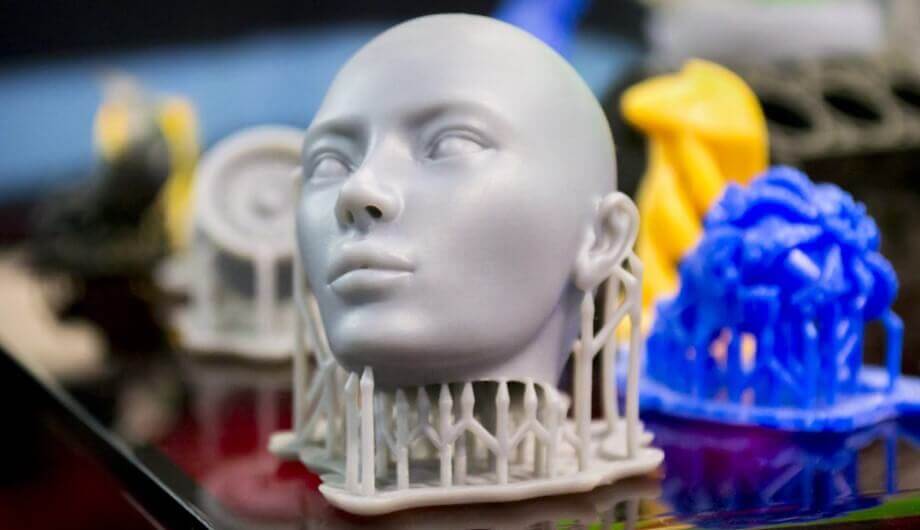
What is the difference between DLP, LCD and SLA light curing 3D PRINTER?
[DLP light curing|LCD light curing|SLA light curing] Light curing 3D Printer: The basic principle of light curing 3D printer technology is to use the accumulation of resin materials to shape, scan the liquid photosensitive resin with a beam of light of a certain wavelength, and transform the three-dimensional object The shape of the laser is decomposed into several flat layers, and each layer of liquid photosensitive resin is scanned and solidified. However, the place where no beam is irradiated is still liquid. Finally, each layer is combined into the desired finished product, and the material utilization rate is close to 100%.
There are many different 3D printing technologies on the market. Familiarizing yourself with the differences between each technology can help clarify what you can expect from your desired print in the end, and thus determine which technology is right for your specific needs. LCD, DLP and SLA 3D printing technologies are the three most common processes for 3D printing using photosensitive resins. Resin 3D printers are widely used to produce high-precision prototypes and parts made from a range of advanced materials with excellent functionality and smooth surface finish.These technologies used to be complicated and costly, but because the technology has matured, today’s small desktop LCD, DLP or SLA 3D printers are cheaper than ever and produce industrial-quality parts that can be printed thanks to the wide variety of materials to choose from Objects can cater to different needs.
Basic knowledge of 3D printing: how to choose FDM and photocuring 3D printing technology
Contents of this article:
- What is light curing 3D printing technology
- What is LCD 3D printing technology
- What is DLP 3D printing technology
- What is an SLA 3D printer
- What is the main difference between DLP and SLA light curing 3D Printer?
- Are the printing materials used in SLA, DLP and LCD 3D light-curing 3D Printers different?
- Post-processing for SLA, DLP and LCD printed models
- The advantages and disadvantages of using light curing
- SLA, DLP and LCD 3D printing technology applications
What is light curing 3D PRINTER 3D printing technology
image source: all3dp
Light-curing 3D printers are commonly divided into three types of light-curing 3D printers: DLP, LCD, and SLA.
Some people may have heard of Stereolithography 3D Printer, but they don’t know that Stereography 3D Printer is also divided into SLA , LCD and DLP. So what’s the difference between them?
First of all, let me talk about what is light-curing 3D printing technology. Its principle is to print objects layer by layer. As for the printing material used, it is different from the rolls of glue of FDM 3D Printer. The printing material used by photocuring 3D Printer is liquid photosensitive resin. This photosensitive resin will react chemically and cure when exposed to light. Photocuring 3D Printer is to print out a solid model by shooting light onto liquid photosensitive resin. In terms of precision, the objects printed by photo-curing technology are more detailed than those printed by FDM or other printing printing technologies, and are suitable for making fine models, such as jewelry prototypes, fine parts, and so on.
The principle of light-curing 3D printing technology is often divided into two types, namely surface curing of DLP and LCD printing technology and point curing of SLA printing technology. The main difference between these two 3D printing technologies is that they shoot light to the photosensitive resin of the printing material. One way is to solidify in the form of a surface, and the other is to solidify in the form of a point.
What is LCD 3D PRINTER 3D printing technology
LCD 3D Printer printing technology: The optical system forms strong light into three beams of R, G, and B through the beam splitter, each of which passes through the RGB three-color liquid crystal panel. Modulate the signal source through AD conversion and add it to the LCD panel. The opening and closing of the optical path can be controlled by controlling the switch of the liquid crystal unit. The RGB light is finally gathered in the prism, and the projection lens is projected on the screen to form a color image, thereby curing the photosensitive resin in a controlled manner.
LCD 3D printing is also known as Mask Stereolithography or MSLA. This technology utilizes an ultraviolet light source from an LED lamp that shines onto the LCD screen. LCD screens are used as masks to generate images of each layer. This will cure the entire layer at one time, so LCD light-curing 3D printers and DLP light-curing 3D printers are all one-time curing of the image of each layer. After the first layer is printed, the printing platform and the object to be printed will be raised simultaneously, and then the LED will project the shape pattern of the next layer of 3D model onto the photosensitive resin, so that the layered printing will finally be completed. Objects are printed. It is worth mentioning that the printed object is printed upside down, which is different from the FDM printing technology.
On the other hand, some current LCD light-curing 3D printers are more AI-intelligent. For example, the HeyGears UltraCraft Reflex LCD 3D printer provides a variety of AI intelligent computing smart functions, such as automatically heating the resin tank, identifying the resin type, monitoring the resin level, and automatic resin filling when necessary, automatic optimization of support structure exposure times, and one-click slice printing make printing easy and efficient.
What is DLP 3D PRINTER 3D printing technology
image source: Flashforge
DLP 3D Printer printing technology: digital light processing rapid prototyping technology. The basic principle is to use digital light source to project layer by layer on the surface of liquid photosensitive resin in the form of surface light, and then solidify and shape layer by layer. DLP technology has many similarities with SLA, and its working principle is also characterized by the use of liquid photosensitive polymers to cure under light. DLP technology uses a higher-resolution digital light processor (DLP) to solidify the liquid polymer, layer by layer, and so on, until the final model is complete. Because LCD prints a single image of each layer onto the platform using a projector fluorescent light that shines light on it, the image on each layer is formed by tiny squares called pixels.
The DLP (Direct Light Processing) light-curing 3D Printer has a built-in light projector. The DLP 3D printer uses the projector to project light onto the photosensitive resin of the printing material to cure the resin. Due to the layered printing, the 3D model will be cut horizontally into layers by the 3D printing software, and then use the DLP projector to project the light of the shape and pattern of the first layer of 3D model onto the liquid photosensitive resin layer by layer, so that the photosensitive Resin light curing and molding.
What is SLA 3D PRINTER 3D printing technology
SLA 3D printing technology: the full name is Stereo Lithography Appearance, which uses laser to focus on the surface of the light-cured material, so that it is sequentially solidified from point to line, from line to surface, and goes round and round, so that layers are superimposed to form a three-dimensional entity.
As for the SLA (Stereolithography) 3D printing technology, it does not use a light projector, but shoots laser light onto the liquid photosensitive resin through a laser, and solidifies the photosensitive resin layer by layer to finally obtain the shape of the entire object. When the SLA light-curing 3D printer emits laser light, it will not shoot out the pattern of a whole layer of 3D model like a DLP machine, but will shoot it point by point onto the liquid resin to form a cured layer. The main components of SLA 3D printer are similar to those of LCD/DLP printers, including a lifting printing platform. When the first layer of photosensitive resin is solidified, the platform will rise a certain distance, and then use laser to print the second layer, and so on. Layers are printed layer by layer, and finally a single overall shape is printed. Another container holds liquid photosensitive resin. In addition, SLA uses two motors, one on the X-axis and the other on the Y-axis. The motor will aim the laser at the specified printing coordinates to solidify the resin at that place. Through 3D slicing software, the 3D model will analyze a series of points and lines with different coordinates, and SLA will accurately hit the laser on the liquid resin of the printing material according to the coordinate path.
Since the light projection method of SLA light curing 3D printer and LCD/ DLP light curing 3D printer is different, the time required for SLA printing will be longer, especially when printing large objects, the printing time used by LCD/ DLP light curing 3D Printer will be much shorter.
What is the main difference between SLA, DLP and LCD light curing 3D PRINTER?
- The main difference between LCD, DLP and SLA stereolithography 3D printers is the light source. SLA generally uses a UV laser beam, while LCD and DLP use UV light from a projector.
- In LCD and DLP, the UV light source remains stationary and cures the entire resin layer at once. In SLA, a laser beam tracks and moves between points of the geometry to be printed.
- Since the LCD and DLP light-curing 3D printer cures the entire resin layer at one time, the DLP runs faster and greatly reduces the 3D printing time.
- LCD and DLP light-curing 3D printers are suitable for making multiple identical parts at one time.
- As for the LCD 3D Printer, the LCD light-curing 3D Printer uses a series of UV LED lamps as the light source. The XY resolution of the LCD 3D Printer is defined by the pixel size of the LCD screen. For example, the pixel size of a 4K LCD 3D Printer is 4096×2160. Light from a flat LCD screen is directed in parallel to the light-curable resin. Since this light is not spread out, pixel distortion is less of an issue for LCD printing. The printing quality of LCD light curing 3D Printer depends on the density of its LED lights. The higher the number of pixels, the better the print quality. This clearly shows that print quality does not depend on changes in model size after projection. Instead, it depends on the LED light density.
Compared with SLA, the common advantage of DLP and LCD stereolithography 3D printers is build speed. Both technologies, DLP and LCD, typically produce parts faster because entire layers are cured at once, rather than individual spots.
The figure below shows the difference between SLA, DLP and LCD printing:
Image source: theorthocosmos
As for the SLA 3D Printer, because it uses laser beams, the printable volume of the SLA 3D printer is independent of the printing resolution. A single print can be printed at any size anywhere within the printable area. Therefore, if you print some large-volume models, the printing time will be longer than that of DLP and LCD light-curing 3D printers.
image source: Flashforge
Are the printing materials used in SLA, DLP and LCD light-curing 3D PRINTER different?
At present, general light-curing 3D printers use light-curing resin at a wavelength of 405nm, so technically any light-curing resin within this range can be used. But in fact, some light-curing resins are divided into SLA, DLP and LCD light-curing 3D Printers, so pay attention when purchasing. For example, SLA uses a more powerful beam than LCD 3D printers, so if you use SLA resin in an LCD 3D printer, it will still cure, but it will take a very long time. If LCD resin is used in an SLA 3D printer, the resin will cure too quickly and details will be lost. The light-curing 3D Printer of LCD technology needs to use low-power LED light source. It is therefore recommended to use resins that can cure quickly with relatively low power light sources. LCD light curing 3D printers will produce better results with these fast curing resins. On the other hand, the light source for DLP is different from others, so it is impossible to predict the curing behavior of a specific resin without testing it.
Resin 3D printing materials have different compositions and performance characteristics. Resin materials include ABS-like materials. This ABS-like material has the excellent mechanical properties of ABS, such as impact resistance, and is suitable for manufacturing functional parts and molds. There are also some high-temperature resistant resin 3D printing materials that are often used in the manufacturing of parts in high-temperature environments, such as in the automotive field.
In addition, there are biocompatible resin suitable for certain medical applications. In addition, light-curing materials also include flexible materials, which have excellent elasticity and ductility and are used to make elastic parts. With the continuous advancement of science and technology, more new varieties of resin materials will be born in the future to meet the needs of various special applications.
Post-processing for SLA, DLP and LCD printed models
For 3D printing models using SLA, DLP and LCD light curing technology, the post-processing process is a very important part. This process mainly includes two steps: post-curing and washing.
During the initial photocuring process, the surface of the model may have been cured, but there is still uncured liquid resin inside. Secondary curing uses a stronger UV light source to fully illuminate the model, so that the internal resin can also fully cure. This not only greatly improves the mechanical strength and heat resistance of the model, but also enhances its service life.
Before secondary curing, the remaining uncured resin on the surface and inside of the model needs to be carefully cleaned. Usually use isopropyl alcohol or special cleaning fluid to soak the model, shake or brush repeatedly until the surface is free of any stickiness. This step is called soaking and is key to ensuring model quality.
If the secondary curing is insufficient, the strength and performance of the model will decrease; if the soaking is not thorough, uncured resin will be left, affecting the surface quality and service life of the model. Therefore, appropriate post-processing processes and parameter settings are crucial to obtain high-quality 3D prints.
In actual operation, the secondary curing time and light intensity, the selection and replacement frequency of the immersion solution all need to be flexibly adjusted according to the specific 3D printing technology and materials.
Post-processing is a key link for the success of 3D printing and requires sufficient attention. Only by mastering the relevant skills can we ensure the high quality of the final 3D printed model.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Stereocuring 3D PRINTER
Light-curing 3D Printer can produce very delicate and highly detailed models, so it is suitable for making jewelry, Figure dolls and other small models that require high details. But if you want to make functional parts, FDM printing technology will have more advantages than light curing technology, because FDM 3D printing material selection breadth is much wider than light curing. Moreover, there are relatively many post-processing procedures for finished products printed with SLA, DLP and LCD light curing, including the need to remove the support on the model, the model needs to be cleaned and post-cured.
SLA, DLP and LCD 3D printing technology applications
Whether it is SLA, DLP or LCD light curing technology, these technologies are widely used in the dental, jewelry and engineering industries. Of course, there are also quite a few enthusiasts who use light curing technology to print some toy models and so on.
LCD is a relatively new technology that has so far been found primarily in relatively inexpensive desktop printers. In general, LCD 3D printers are cheaper to use than DLP or SLA 3DPrinters because LCD 3D printers can have cheaper components such as LCD screens, making them a cheaper resin 3D printing solution. This is a great thing, as it expands the reach of resin 3D printing to the general public.
FAQs about LCD, DLP, SLA light curing technology
Q1: What are the advantages of DLP and LCD over SLA light curing technology?
In terms of printing speed, LCD 3D printers and DLP 3D printer is much faster than SLA 3D printer, because LCD and DLP 3D printers will cure a whole layer of photosensitive resin every time it projects light. On the other hand, LCD light-curing 3D printers are very mature, so they are cheaper and more widely used than DLP light-curing 3D printers.
Q2: What are the similarities between DLP and LCD light curing technology?
Both DLP and LCD cure each layer of photosensitive resin as a whole, while the laser of SLA cures the photosensitive resin point by point, so the speed of DLP and LCD printing technology will be much faster than that of SLA technology.
Q3: What is the principle of light curing 3D printer?
The basic principle of light-curing 3D printer technology is to use the accumulation of resin materials for molding, scan the liquid photosensitive resin with a beam of certain wavelength, decompose the shape of the three-dimensional object into several flat layers, and make each layer of liquid photosensitive resin cured after scanning. However, the place where no beam is irradiated is still liquid, and finally the various layers are combined into the desired finished product, and the material utilization rate is close to 100%.
Q4: What post-processing is required for SLA, DLP and LCD 3D printed models?
The post-processing process of SLA, DLP and LCD light curing technology mainly includes two steps: post-curing and washing. After that, it needs to be sanded to remove the support structure.